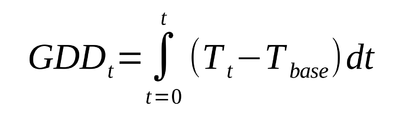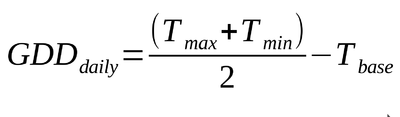Difference between revisions of "Growing Degree Day"
(→Introduction) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
| − | In addition to the value of T<sub>base</sub>, the selection of t=0 will also change the value of accumulated GDD: | + | In addition to the value of T<sub>base</sub>, the selection of the start date (t=0) will also change the value of accumulated GDD. Common start dates are: |
#Coldest day of the year | #Coldest day of the year | ||
#Shortest day of the year | #Shortest day of the year | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
In addition to selection of T<sub>base</sub>, T<sub>cap</sub> and and when t=0, | In addition to selection of T<sub>base</sub>, T<sub>cap</sub> and and when t=0, | ||
different methods exist for calculating heat units depending on a) the crop or biological | different methods exist for calculating heat units depending on a) the crop or biological | ||
| − | organism of interest and b) the whim or personal preference of the researcher. | + | organism of interest and b) the whim or personal preference of the researcher. |
==NOAA Modified Growing Degree Day Formula== | ==NOAA Modified Growing Degree Day Formula== | ||
The method most commonly used in the U.S. for approximating GDD for phenology is the formula first suggested by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The “modified growing degree day formula” calculates daily accumulation of GDD’s as the average daily temperature minus 50° F. | The method most commonly used in the U.S. for approximating GDD for phenology is the formula first suggested by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The “modified growing degree day formula” calculates daily accumulation of GDD’s as the average daily temperature minus 50° F. | ||
| − | + | This method of approximating GDD for each day is the average of the daily maximum and minimum temperatures above T<sub>base</sub>. | |
[[File:GDD average.png|frameless|center|400px]] | [[File:GDD average.png|frameless|center|400px]] | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
When comparing GDD numbers from different sources, one must consider: | When comparing GDD numbers from different sources, one must consider: | ||
| − | #Are the base temperatures (T<sub>base</sub>) the same? | + | #Are the base temperatures (T<sub>base</sub>) and the cap temperatures (T<sub>cap</sub>) the same? |
#Are the start dates (t<sub>0</sub>) for the accumulation the same? | #Are the start dates (t<sub>0</sub>) for the accumulation the same? | ||
#Are the equations used to calculate the daily GDD the same? | #Are the equations used to calculate the daily GDD the same? | ||
| − | #Are the temperatures used in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit? | + | #Are the temperatures used in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit? |
==SQL calculation of GDD== | ==SQL calculation of GDD== | ||
Latest revision as of 07:53, 26 November 2018
Contents
Introduction
Plants grow in a cumulative stepwise manner which is strongly influenced by ambient temperature. Growing Degree Days (GDD), also called Growing Degree Units (GDU) or Heat Units (HU), are based on the observation that within limits, plants grow faster when warm and more slowly when cold. Below a base temperature (Tbase), the plant is dormant and little growth occurs. Since growth depends on the accumulation of specific quantities of heat, by accumulating Growing Degree Days it is possible to predict when events such as bud break (nectar flows) will occur during a growing season regardless of differences in temperatures from year to year.
A simple theoretical formula for GDD at time t is:
where:
Tt = temperature at time t
Tbase = temperature below which plant growth is zero.
In addition to the value of Tbase, the selection of the start date (t=0) will also change the value of accumulated GDD. Common start dates are:
- Coldest day of the year
- Shortest day of the year
- Arbitrary Gregorian calendar date (e.g. January 1)
Each plant species has it's own upper air temperature threshold, Tcap.
At temperatures above Tcap the plant does not grow any faster. Tcap varies for each species.
In addition to selection of Tbase, Tcap and and when t=0, different methods exist for calculating heat units depending on a) the crop or biological organism of interest and b) the whim or personal preference of the researcher.
NOAA Modified Growing Degree Day Formula
The method most commonly used in the U.S. for approximating GDD for phenology is the formula first suggested by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The “modified growing degree day formula” calculates daily accumulation of GDD’s as the average daily temperature minus 50° F.
This method of approximating GDD for each day is the average of the daily maximum and minimum temperatures above Tbase.
Before calculating the average:
- Any temperature below Tbase is set to Tbase.
- Any temperature above Tcap is set to Tcap.
If the mean daily temperature is lower than the base temperature then GDD=0.
Some warm temperate and tropical plants have significant requirements for days above 30 °C to mature fruit or seeds.
When comparing GDD numbers from different sources, one must consider:
- Are the base temperatures (Tbase) and the cap temperatures (Tcap) the same?
- Are the start dates (t0) for the accumulation the same?
- Are the equations used to calculate the daily GDD the same?
- Are the temperatures used in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit?
SQL calculation of GDD
Centigrade Tbase = 10 Tmax = 30
SET @gdd_total:=0; SELECT q1.doy, q1.gdd, round(@gdd_total := @gdd_total + q1.gdd) as gdd_tot FROM (SELECT DAYOFYEAR(DATE_FORMAT(`hive_observation_time_local`, '%Y-%m-%d')) AS doy, (least(greatest(max(wx_temp_c),10),30) - least(greatest(min(wx_temp_c),10),30))/2 AS gdd from HIVE_DATA where hive_id=10 group by DATE_FORMAT(`hive_observation_time_local`, '%Y-%m-%d') ) AS q1
SELECT hive_id, DAYOFYEAR(DATE_FORMAT(`hive_observation_time_local`, '%Y-%m-%d')) AS doy, (least(greatest(max(wx_temp_c),10),30) - least(greatest(min(wx_temp_c),10),30))/2 AS gdd from HIVE_DATA group by DATE_FORMAT(`hive_observation_time_local`, '%Y-%m-%d'), hive_id