Difference between revisions of "Education and Bee Science"
(→Measure the effect of stressors on bees) |
(→Spring 2016) |
||
| (38 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[File:RGNS mites.jpg|thumb|right|700px|frame| | [[File:RGNS mites.jpg|thumb|right|700px|frame| | ||
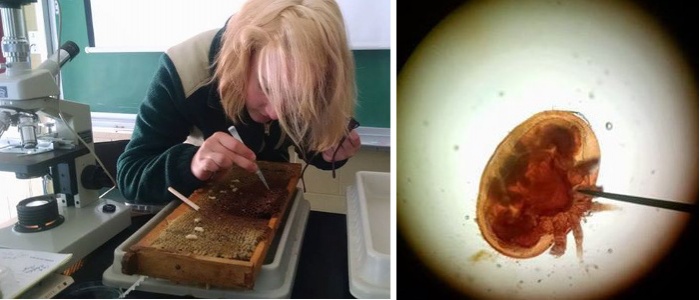
A student observes varroa mites while extracting honey. Varroa mites captured from drone brood pulled from a frame of honey (L) are viewed under a microscope (R).]] | A student observes varroa mites while extracting honey. Varroa mites captured from drone brood pulled from a frame of honey (L) are viewed under a microscope (R).]] | ||
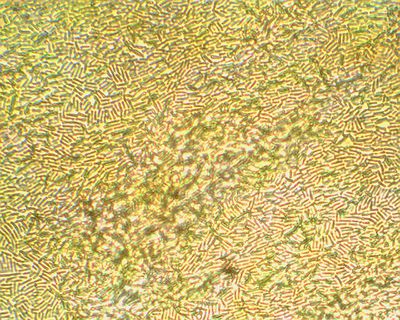
| − | [[File:Lactobacillus 2.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[File:Lactobacillus 2.jpg|thumb|right|400px|frame|Lactobacillus cultured from bee gut.]] |
</div> | </div> | ||
==Goal== | ==Goal== | ||
| − | An early goal of Hivetool has been to attract students to Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM) by getting bee science into the classroom. Bee science includes agriculture, biology, botany, chemistry, computing, food, industrial arts, math, physics, programming, statistics – in short, something for everyone. | + | An early goal of Hivetool has been to attract students to Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM) by getting bee science into the classroom. Bee science includes agriculture, biology, botany, chemistry, computing, food, industrial arts, math, physics, programming, statistics – in short, something for everyone. Experiments introduce students to a number of STEM projects and allow hands on experiences in design, research, data gathering and analysis. Labor intensive studies that are suited for a student workforce are selected. |
| + | |||
| + | This project based approach allows for multiple learning styles and reinforces theory that the students are taught in class. Real world projects are designed to foster an appreciation for and an understanding of how science is conducted in the real world. Pedagogically it also presents a way to have students do significant scientific hands on research instead of just learning about science from a text or lecture. | ||
==Bees in the Classroom== | ==Bees in the Classroom== | ||
| − | In 2011, Blue Ridge Honey Company donated a hive to be set up as an observation hive on the campus of Rabun Gap-Nacoochee School. Instead of a classical observation hive, it was set up as an 21st century observation hive, on a scale, with temperature sensors, camera and microphone. It is designated GA004 with NASA's Honey Bee Net. | + | In 2011, the [https://www.facebook.com/Blue-Ridge-Honey-Company-108518912565034/ Blue Ridge Honey Company] donated a hive to be set up as an observation hive on the campus of Rabun Gap-Nacoochee School. Instead of a classical observation hive, it was set up as an 21st century observation hive, on a scale, with temperature sensors, camera and microphone. It is designated GA004 with NASA's Honey Bee Net. |
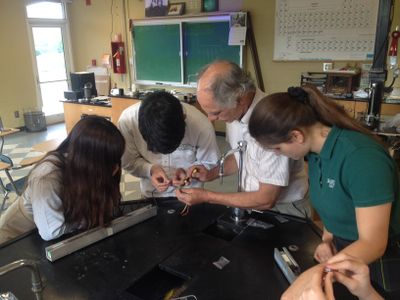
For the last four years, during the first week of classes, students extract honey from the hives. The bees and products from the hive are used for [[RGNS|science experiments]], fund raising and student activities.<br> | For the last four years, during the first week of classes, students extract honey from the hives. The bees and products from the hive are used for [[RGNS|science experiments]], fund raising and student activities.<br> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[File:RGNSpullhoney2.png|thumb|right|400px|Students pull honey and inspect hives. May 2017]] | ||
[[File:RGNS extraction.jpg|thumb|400px|right|Students extract honey.]] | [[File:RGNS extraction.jpg|thumb|400px|right|Students extract honey.]] | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:January 15 012.JPG|thumb|right|400px|[http://centerforhoneybeeresearch.org/w/index.php?title=Lab_Experiment_I._Effect_of_a_common_agricultural_herbicide_on_honey_bee_gut_bacteria_%28Small_Replicates%29 Bees in Solo cup cages being fed glyphosate.]]] |
| + | [[File:Bee boxes 010.JPG| thumb|right|400px|[http://centerforhoneybeeresearch.org/w/index.php?title=Lab_Experiment_II._Effect_of_a_common_agricultural_herbicide_on_honey_bee_gut_bacteria_%28Medium_Replicates%29 Bee cages in incubator. Medium size replicates]]] | ||
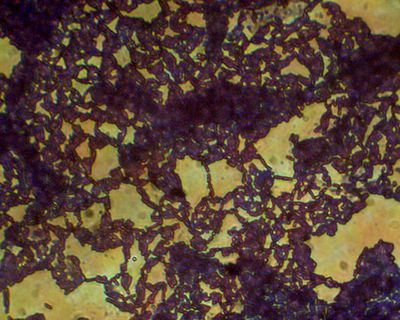
[[File:Bee gut culture.jpg| thumb|right|400px|Bee gut bacteria culture.]] | [[File:Bee gut culture.jpg| thumb|right|400px|Bee gut bacteria culture.]] | ||
[[File:Lactobacillus 1.jpg| thumb|right|400px|Lactobacillus from bee gut culture.]] | [[File:Lactobacillus 1.jpg| thumb|right|400px|Lactobacillus from bee gut culture.]] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 25: | ||
[[File:IMG 3845.JPG|thumb|400px|right|AP Physics students assemble hive scale.]] | [[File:IMG 3845.JPG|thumb|400px|right|AP Physics students assemble hive scale.]] | ||
[[File:RGNS scale build2.JPG|thumb|400px|right|AP Physics students assemble hive scale.]] | [[File:RGNS scale build2.JPG|thumb|400px|right|AP Physics students assemble hive scale.]] | ||
| + | |||
===Spring 2012=== | ===Spring 2012=== | ||
| + | A hive donated by the Blue Ridge Honey Company was set up as a 21st century observation hive on the campus of Rabun Gap-Nacoochee School. It was placed on an electronic scale and connected to the internet. | ||
===Fall 2012=== | ===Fall 2012=== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 37: | ||
| − | Three projects using the bees were entered in the [[RGNS|Rabun Gap-Nacoochee School 2012-2013 Science Symposium]]. | + | Three projects using the bees were entered in the [[RGNS#Rabun_Gap-Nacoochee_School_2012-2013_Science_Symposium|Rabun Gap-Nacoochee School 2012-2013 Science Symposium]]. |
The results of their findings were presented at a Macon County Beekeepers Association meeting. | The results of their findings were presented at a Macon County Beekeepers Association meeting. | ||
| Line 52: | Line 58: | ||
In the fall of 2015, over 300 pounds of honey was extracted. and most of it sold in one pound jars to parents for $10 a jar. | In the fall of 2015, over 300 pounds of honey was extracted. and most of it sold in one pound jars to parents for $10 a jar. | ||
| − | A series of talks, presentations and hands on activities were conducted for three classes who participated in extracting honey. | + | A series of talks, presentations and hands on activities were conducted for three classes who participated in extracting honey. A course, Botany, Entomology and Microbiology was offered. The course consisted of Botany field trips in the fall, microbiology lab experiments in the winter. Five electronic scales were assembled. |
===Winter 2016=== | ===Winter 2016=== | ||
Lab experiments were conducted to measure the effect of glyphosate on honey bee gut bacteria. | Lab experiments were conducted to measure the effect of glyphosate on honey bee gut bacteria. | ||
| − | [http:// | + | [http://hivetools.net/w/index.php?title=Lab_Experiment_II._Effect_of_a_common_agricultural_herbicide_on_honey_bee_gut_bacteria_%28Medium_Replicates%29 Effect of a common agricultural herbicide on honey bee gut bacteria] |
| + | |||
| + | ===Spring 2016=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://datacenterforhoneybeeresearch.org/w/index.php?title=Field_Experiment_I._Environmental_Pesticide_Concentrations Field experiments measured insecticide, fungicide and herbicide levels in hives] at three locations: pristine, urban and agricultural as part of the Long Term Environmental Research Program at Rabun Gap Nacoochee School. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Fall 2016=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the fall of 2016, over 300 pounds of honey was extracted. and most of it sold in one pound jars to parents for $10 a jar. | ||
| + | A series of talks, presentations and hands on activities were conducted for classes who participated in extracting honey. A three trimester course, Botany, Entomology and Microbiology was again offered. The RGNS apiary has been built up to 12 hives. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Spring 2017=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | After wintering the hives in Unadilla, Georgia, 80 lbs of honey was extracted and sold. The RGNS apiary now consists of 17 hives | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Fall 2017=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Due to student demand, two sessions of Botany, Entomology and Microbiology are being taught. 624 pounds of honey were harvested, bottled and sold. Bee venom was collected and tested for antibacterial properties. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Fall 2018=== | ||
==Uses in the Curriculum== | ==Uses in the Curriculum== | ||
| Line 65: | Line 90: | ||
Lab procedures and protocols are being developed: | Lab procedures and protocols are being developed: | ||
| − | *[http:// | + | *[http://datacenterforhoneybeeresearch.org/w/index.php?title=Lab_Experiment_II._Effect_of_a_common_agricultural_herbicide_on_honey_bee_gut_bacteria_%28Medium_Replicates%29 Effect of a common agricultural herbicide on honey bee gut bacteria] |
*[http://onsnetwork.org/rgns/ Effects of Glyphosate on Honey Bee Gut Bacteria (Class notes)] | *[http://onsnetwork.org/rgns/ Effects of Glyphosate on Honey Bee Gut Bacteria (Class notes)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Field experiments: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[http://datacenterforhoneybeeresearch.org/w/index.php/Field_Experiment_I._Environmental_Pesticide_Concentrations Environmental Pesticide Concentrations] | ||
====Parasites==== | ====Parasites==== | ||
Latest revision as of 14:48, 7 February 2019
Contents
Goal
An early goal of Hivetool has been to attract students to Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM) by getting bee science into the classroom. Bee science includes agriculture, biology, botany, chemistry, computing, food, industrial arts, math, physics, programming, statistics – in short, something for everyone. Experiments introduce students to a number of STEM projects and allow hands on experiences in design, research, data gathering and analysis. Labor intensive studies that are suited for a student workforce are selected.
This project based approach allows for multiple learning styles and reinforces theory that the students are taught in class. Real world projects are designed to foster an appreciation for and an understanding of how science is conducted in the real world. Pedagogically it also presents a way to have students do significant scientific hands on research instead of just learning about science from a text or lecture.
Bees in the Classroom
In 2011, the Blue Ridge Honey Company donated a hive to be set up as an observation hive on the campus of Rabun Gap-Nacoochee School. Instead of a classical observation hive, it was set up as an 21st century observation hive, on a scale, with temperature sensors, camera and microphone. It is designated GA004 with NASA's Honey Bee Net.
For the last four years, during the first week of classes, students extract honey from the hives. The bees and products from the hive are used for science experiments, fund raising and student activities.
Spring 2012
A hive donated by the Blue Ridge Honey Company was set up as a 21st century observation hive on the campus of Rabun Gap-Nacoochee School. It was placed on an electronic scale and connected to the internet.
Fall 2012
Students extracted honey from the hive.
Spring 2013
Three projects using the bees were entered in the Rabun Gap-Nacoochee School 2012-2013 Science Symposium.
The results of their findings were presented at a Macon County Beekeepers Association meeting.
A 60 inch high definition TV was installed in the entrance to the Morris Brown Science Building can stream live bee activity and hive weight.
Fall 2013
In the fall of 2013, 70 pounds of honey was extracted. and sold in one pound jars to parents for $10 a jar.
During the extraction, a frame of drone brood that was in the honey super was examined for varroa mites.
Fall 2014
In the fall of 2014, 170 pounds of honey was extracted. and sold in one pound jars to parents for $10 a jar.
During the extraction, a frame of drone brood that was in the honey super was examined for varroa mites.
Fall 2015
In the fall of 2015, over 300 pounds of honey was extracted. and most of it sold in one pound jars to parents for $10 a jar. A series of talks, presentations and hands on activities were conducted for three classes who participated in extracting honey. A course, Botany, Entomology and Microbiology was offered. The course consisted of Botany field trips in the fall, microbiology lab experiments in the winter. Five electronic scales were assembled.
Winter 2016
Lab experiments were conducted to measure the effect of glyphosate on honey bee gut bacteria. Effect of a common agricultural herbicide on honey bee gut bacteria
Spring 2016
Field experiments measured insecticide, fungicide and herbicide levels in hives at three locations: pristine, urban and agricultural as part of the Long Term Environmental Research Program at Rabun Gap Nacoochee School.
Fall 2016
In the fall of 2016, over 300 pounds of honey was extracted. and most of it sold in one pound jars to parents for $10 a jar. A series of talks, presentations and hands on activities were conducted for classes who participated in extracting honey. A three trimester course, Botany, Entomology and Microbiology was again offered. The RGNS apiary has been built up to 12 hives.
Spring 2017
After wintering the hives in Unadilla, Georgia, 80 lbs of honey was extracted and sold. The RGNS apiary now consists of 17 hives
Fall 2017
Due to student demand, two sessions of Botany, Entomology and Microbiology are being taught. 624 pounds of honey were harvested, bottled and sold. Bee venom was collected and tested for antibacterial properties.
Fall 2018
Uses in the Curriculum
Biology
Measure the effect of stressors on bees
Lab procedures and protocols are being developed:
Field experiments:
Parasites
Introduced invasive pests, disease vectors, integrated pest management
Varroa mites (Varroa destructor) are small, reddish-brown tick like pests which feed on the hemolymph ("blood") of the honey bees. The feeding of the mites on the bee opens wounds which are sites for possible infection. In addition, the mite will infect the bee with viruses. Tracheal mites are microscopic mites which reproduce in the trachea (airways) of the bee.
- Assess varroa mite levels in the hive using a sticky board.
- Assess varroa mite wound damage and tracheal mite infestation using a dissecting microscope.
- Determine the cost/benefits of different mite controls: formic acid, thymol, Taktic, cumophos
- Design, test and implement a pest control policy.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) amplification
- DNA Barcoding for Honey Biodiversity
- Development of primer and probe sets for the detection of plant species in honey
- Tracking Plant, Fungal, and Bacterial DNA in Honey Specimens
Bioacoustics
Botany
Melissopalynology - food source and quality
- Collect voucher specimens from a 2 mile radius of the hive.
- Use GPS and/or google maps to locate the nectar and pollen sources.
- Prepare slides, make photomicrographs, build an online pollen database.
- Take pollen and nectar samples from hive. Identify source of nectar flow.
- Identify and count pollen in local and commercial honey.
- Greg Bisbee's Arrowhead High School Pollen Lab.
- University of Arizona Catalog of Internet Pollen and Spore Images
- Science & Plants for Schools - Pollen Image Library
- Radboud University Virtual Classroom Pollen - Shape, Color & Size
- USDA, ARS, APMRU, Pollen Lab Pollen as Indicators of Source Areas and Foraging Resources
Horticulture/Phenology
Use ambient temperature data from the hive to calculate Growing Degree Day (GDD) to predict nectar flow.
Chemistry
- Test for sugar adulteration.
- Test for Insecticides/Fungicides
- Test for Pure Honey
- Sugar Syrups optical activity - circular polarization - helical molecules
- Rotating Light
- Peter Keusch's Test for Amylase in Bee Honey
- Peter Keusch's Fehling's Test
- Peter Keusch's Artificial Honey - Formation of a Sweet Imitation
Physics
- Strain Gages
- Load Cells
- Bridge, voltage divider
- Differential Input
- Analog to Digital Converter
Communication
- Write research grant proposals and present to State Beekeepers Assoc.
- Publish research
Computers
- Interface instruments to computer
- Logging
- Web server setup and administration
- Data base server setup and administration
Video
- <a href=http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/VAIB08PAPERS/vaib9_mummert.pdf>Intel Research Pittsburgh, Video Monitoring of honey Bee Colonies</a>
- <a href=http://opencv.willowgarage.com/wiki/>Open Computer Vision</a>
- Zoneminder
- Timelapse
- <a href=http://www.classifynder.com/sites/default/papers/CraigThesis1.pdf>Automation of Pollen Analysis using a Computer</a>
Math/Programing
- Calibrate instruments - linear scaling, regression.
- Statistics.
- Audio analysis - time domain/frequency domain, Fourier transform.
- Audio synthesis - waveforms, sine wave, square wave
- Graphing - implement graphing software for web server