Difference between revisions of "Hardware: Sensor Wiring"
(→Software) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 214: | Line 214: | ||
==Rain Gauge== | ==Rain Gauge== | ||
| − | + | IMPORTANT: The rain gauge software may require software setup. | |
| + | ===Hardware=== | ||
A "Tipping Bucket" type rain gauge is used. It works by counting the number of times the bucket tips. The Rainwise bucket available in the US dumps every one hundredth (1/100 or .01) inches of rain. | A "Tipping Bucket" type rain gauge is used. It works by counting the number of times the bucket tips. The Rainwise bucket available in the US dumps every one hundredth (1/100 or .01) inches of rain. | ||
| Line 249: | Line 250: | ||
|Digital ground | |Digital ground | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Software=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | For the range gauge to work, the Data Acquisition Daemon (DAD) must be started on boot and the rain gauge reset at midnight by these lines in the crontab: | ||
| + | |||
| + | @reboot /home/hivetool/dad7.sh | ||
| + | 0 0 * * * timeout -s KILL 1m /home/hivetool/rain_reset.sh | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Cron | See the cron page]] for more details of the software needed to read the rain gauge. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | To check if dad is running, run | ||
| + | ps -ef | grep dad | ||
| + | |||
| + | pi@raspberrypi:~ $ ps -ef|grep dad | ||
| + | root 316 287 0 2018 ? 00:00:00 /bin/sh -c /home/hivetool/dad7.sh | ||
| + | root 317 316 0 2018 ? 00:00:00 /bin/bash /home/hivetool/dad7.sh | ||
| + | root 609 317 0 2018 ? 00:04:48 /home/hivetool/dad7 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | To play with the rain gauge, first change to the /home/hivetool directory: | ||
| + | cd /home/hivetool | ||
| + | |||
| + | to see the current rain counts: | ||
| + | cat rain_total.conf | ||
| + | |||
| + | to reset them to zero | ||
| + | ./rain_reset.sh | ||
| + | |||
| + | to watch the count while testing: | ||
| + | watch cat rain_total.conf | ||
Latest revision as of 17:00, 6 January 2019
The Raspberry Pi Hive Interface Board uses modular telephone RJ14 (6P4C) connectors for the sensors. Pins 2, 3, 4, and 5 are used.
Eventually, the load cells will be supplied with the connector attached. Cables will be provided for the other sensors.
These instructions are for developers that use the Raspberry Pi Hive Interface board versions 0.1 - 0.3.
The Registered Jack (RJ) series connectors install using an inexpensive crimping tool.
Contents
RJ Connectors
Crimp on Registered Jack (RJ) plugs are insulation displacement connectors (IDC) that pierce the insulation on the wire, forming a gas tight joint. Some RJ connectors are designed to take round cable, some flat, some both. Some are designed for solid wire, some for stranded, some for both.
The male connectors are called plugs. The female connectors are called jacks. They are designated by the number of positions (P) and the number of contacts (C) that are populated. We are currently using 6P4C (six position, four contact) plugs and jacks.
For a detail description, see Registered Jack on Wikipedia.
Number of Contacts
Contact numbering
Load Cells
| Load Cell Wiring | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| RJ14 Pin | Color | HX711 | Description |
| 2 | Red | OUT+ | Excitation voltage from HX711 voltage regulator |
| 3 | White | A- | A/D channel A negative input |
| 4 | Green | A+ | A/D channel A positive input |
| 5 | Black | GND | Analog ground |
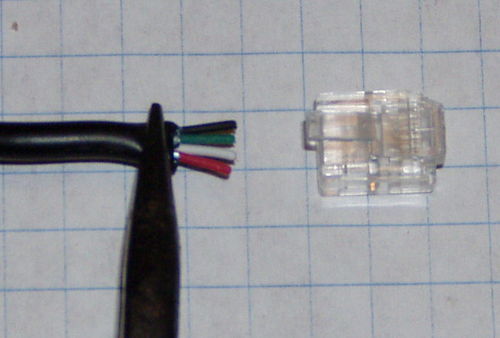
- Remove any heat shrink from the load cell cable.
- Cut off the drain wire.
- Spread out the four wires and arrange them in Red, White, Green, Black order.
- Gently flatten the cable with a pair of pliers.
- Evenly trim the wires so they extend approximately 1/4 inch past the jacket.
- Orient the RJ14 connector so the latch tab is up.
- Insert the wires all the way into the RJ14 connector, making sure that the wires are in the right order.
- Inspect the wires and connector with a magnifier. Make sure the outer jacket is past the strain relief and each wire is all the way to the end of the connector.
- If the wires do not extend the full length of the connector, or the jacket does not go past the strain relief, remove the wire and trim a little of the jacket, or shorten the wires.
- Crimp the connector.
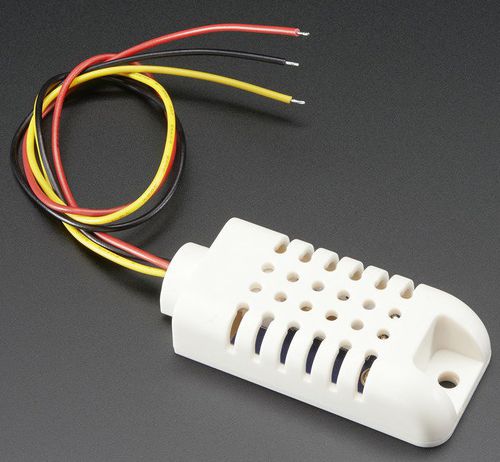
BME680 Temperature,Humidity, Pressure VOCs Sensor
DHT22/AM2302 Temperature and Humidity Sensor
Bare Sensor
| DHT22 Wiring | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| RJ14 Pin | Color | DHT22 Signal | Description |
| 2 | Black | + | +3.3VDC supply |
| 3 | Red | Out | Pi GPIO |
| 4 | Green | No Connect | Not used |
| 5 | Yellow | - | Digital ground |
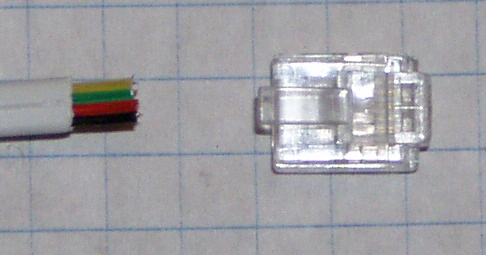
Wire type is standard four conductor flat telephone wire.
Jacket color is not important, recommend light color, avoid black.
Telephone wire colors are Black, Red, Green (not used), Yellow.
Crimp the RJ14 connector for normal telephone use.
Consider cutting a 10 or 12' cord in half for two sensors, crimping will be unnecessary
Trouble shooting:
Make sure the cable is crimped Black, Red, Green, Yellow and not Yellow, Green, Red, Black.
Wired Sensor
The wired sensor is larger and more expensive. It will not fit inside the hive (between the supers) as well as the bare DHT22 sensors.
Wire phone cable Black to DHT22 Red.
Wire phone cable Red to DHT22 Yellow.
Wire phone cable Yellow to DHT22 Black.
| Wired DHT22 Wiring | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RJ14 Pin | Color | DHT22 Signal | DHT22 Color | Description |
| 2 | Black | + | Red | +3.3VDC supply |
| 3 | Red | Out | Yellow | Pi GPIO |
| 4 | Green | No Connect | Not used | |
| 5 | Yellow | - | Black | Digital ground |
DS18B20 Temperature Sensor
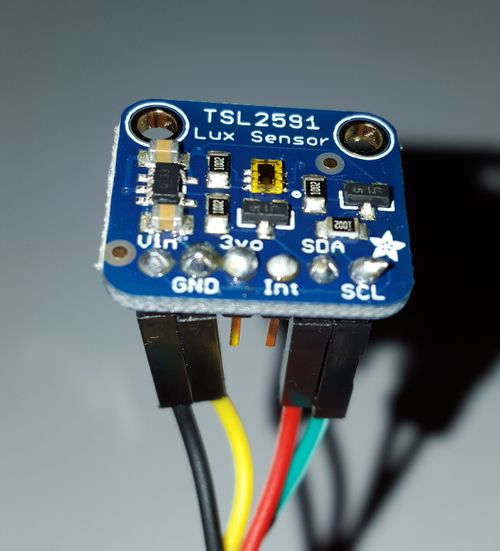
TSL2591 Lux Sensor
| TSL2591 Wiring | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| RJ14 Pin | Color | TSL2591 Signal | Description |
| 2 | Black | Vin | +3.3Volt input |
| 3 | Red | SDA | Pi GPIO 8 I2C SDA |
| 4 | Green | SCL | Pi GPIO 9 I2C SCL |
| 5 | Yellow | GND | Digital ground |
TSL 2591:
3Vo - not used, Int - not used.
Wire type is standard four conductor flat telephone wire.
Jacket color is not important, recommend light color, avoid black
Wire colors are Black, Red, Green, Yellow.
Crimp the RJ14 connector for normal telephone use.
Consider cutting a 10 or 12' cord in half for two sensors, crimping will be unnecessary
TIP
- Do not use a ping pong ball cut in half for a weather shield. They are not UV resistant and will fail in about 6 months.
Rain Gauge
IMPORTANT: The rain gauge software may require software setup.
Hardware
A "Tipping Bucket" type rain gauge is used. It works by counting the number of times the bucket tips. The Rainwise bucket available in the US dumps every one hundredth (1/100 or .01) inches of rain.
Only the Red (input) and Yellow (ground) wires are used. Each time the input is momentarily shorted to ground, the pulse is counted.
Pin 22 on J8, GPIO 6 (wiringPi) or 25 (PIGPIO), is programed as a digital input with a pull up resistor. To prevent false triggers and help debounce the switch, it is filtered by a 1K series resister and a 0.1 bypass capacitor located on the hive interface board.
| TSL2591 Wiring | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| RJ14 Pin | Color | TSL2591 Signal | Description |
| 2 | Black | Not used DNC | +3.3Volt |
| 3 | Red | Rain Gauge Input | Pi GPIO 6 (wiringPi) or 25 (PIGPIO) Pin 22 on J8 |
| 4 | Green | Not used DNC | Pi GPIO ? |
| 5 | Yellow | GND | Digital ground |
Software
For the range gauge to work, the Data Acquisition Daemon (DAD) must be started on boot and the rain gauge reset at midnight by these lines in the crontab:
@reboot /home/hivetool/dad7.sh 0 0 * * * timeout -s KILL 1m /home/hivetool/rain_reset.sh
See the cron page for more details of the software needed to read the rain gauge.
To check if dad is running, run
ps -ef | grep dad
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ ps -ef|grep dad root 316 287 0 2018 ? 00:00:00 /bin/sh -c /home/hivetool/dad7.sh root 317 316 0 2018 ? 00:00:00 /bin/bash /home/hivetool/dad7.sh root 609 317 0 2018 ? 00:04:48 /home/hivetool/dad7
To play with the rain gauge, first change to the /home/hivetool directory:
cd /home/hivetool
to see the current rain counts:
cat rain_total.conf
to reset them to zero
./rain_reset.sh
to watch the count while testing:
watch cat rain_total.conf